Glutathione is associated with children health
On the path of paying attention to the healthy growth of children, the special group of children with special needs always touches the hearts of countless people.
Due to various innate or acquired factors, they face numerous challenges in physical development, cognitive development, immune function and other aspects.
In recent years, glutathione has gradually come into people's view. This seemingly unfamiliar term actually plays an extremely crucial role in our bodies.
health predicaments faced by children with special needs
Special needs children include various types of special groups such as hyperactivity, tics, autism, and developmental delay.

During their growth, they are often accompanied by a series of health problems.
For instance, many children with autism suffer from gastrointestinal dysfunction and poor nutrient absorption, which in turn affects their physical development and brain function.
Or there may be a relatively low immunity, making them vulnerable to various infectious diseases, and the body's inflammatory response may further hinder their neural development.
These health issues are intertwined, posing numerous obstacles to the growth of children with special needs
What exactly is glutathione?
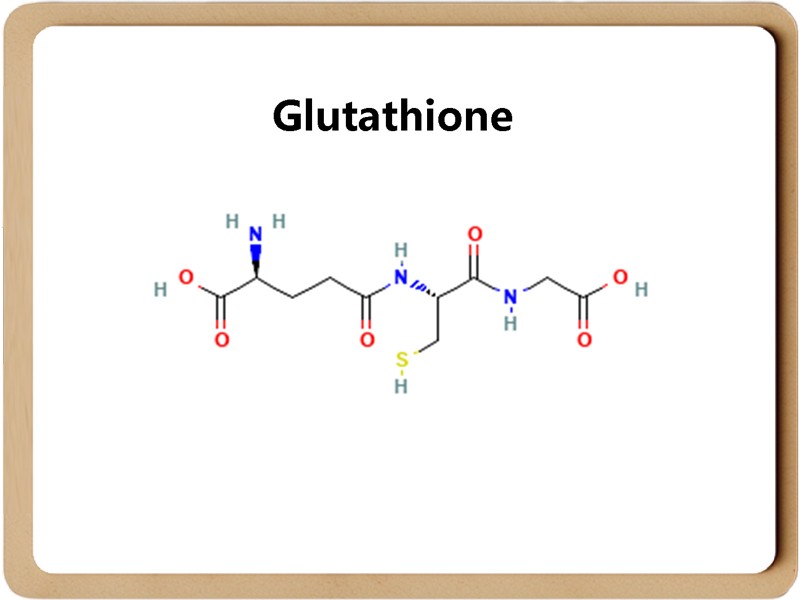
Glutathione, with the English name Glutathione, is usually abbreviated as GSH.
It is a tripeptide small protein composed of glutamic acid, cysteine and glycine. Despite its tiny size, it contains tremendous energy.
Glutathione can be found in almost every cell of our body. It actively participates in various physiological activities within cells and plays an indispensable role in maintaining the normal functions and health of cells.
It is just like a series of "super guards" in our bodies, always safeguarding the safety of cells.
What important roles does glutathione play for children with special needs?
Powerful antioxidant function
Free radicals are everywhere in our living environment.
Whether it is ultraviolet radiation, air pollution, or bad living habits such as smoking and staying up late, all can promote the production of a large number of free radicals in the body.
Children with special needs often produce excessive free radicals in their bodies due to abnormal metabolism or long-term stress.
These free radicals are extremely active, acting like "troublemakers", attacking various biomolecules within cells, including the DNA of healthy cells, causing cell damage. This may have adverse effects on the neurodevelopment, immune system, and organ functions of children with special needs.
Glutathione, as an important antioxidant in the body, can react with free radicals and stabilize them due to its abundant thiol groups, thereby protecting cells from the damage caused by free radicals.
It is like a "shield" for cells, helping us resist the invasion of free radicals and maintain the health and vitality of cells.
Assist in detoxification process
In daily life, the body inevitably comes into contact with various harmful substances, such as environmental pollutants, drug residues, heavy metals, etc.
Children with special needs may have weaker metabolic functions and relatively insufficient detoxification abilities.
These harmful substances are more likely to accumulate in their bodies and cause damage. You can also have a hair heavy metal test to check the metal status of your body.
Glutathione plays a significant role in the detoxification process.
It can combine with heavy metals (such as lead, mercury, etc.), drugs, chemicals and other substances that enter the body, converting them into non-toxic or low-toxic substances, and then be excreted from the body through urine or bile.
When children have poor gastrointestinal conditions, there may be toxins produced by some harmful bacteria in the intestines. Glutathione can help reduce the irritation of these toxins to the intestinal mucosa, improve gastrointestinal function and promote nutrient absorption.
Moreover, the liver is the "detoxification factory" of our body, shouldering the important responsibility of eliminating various toxins and harmful substances within the body.
This detoxification process helps reduce the burden on the liver, protect it from damage and maintain its normal function.
Regulate immune function
Low immunity makes children more prone to illness, and frequent infections, such as respiratory infections, will further increase the burden on the body.
The immune system is the "defense line" of our body against diseases. Glutathione plays an important regulatory role in the immune system. It can regulate the activity of immune cells, promote the proliferation and differentiation of lymphocytes, and enhance the phagocytic ability of macrophages, thereby improving the body's resistance.
Glutathione can also inhibit inflammatory responses, reduce the damage of inflammation to body tissues, and maintain the stability of the internal environment of the body.
Improve metabolic function
The normal metabolism of the body is crucial for children's growth and development. After a child has undergone a urine organic acid test, we can observe the metabolic condition of their body.
Glutathione is involved in the metabolic processes of various substances in the body, such as the metabolism of carbohydrates, fats and proteins, which helps maintain the balance of metabolism in the body and improves metabolic function.
During the process of energy metabolism, glutathione can ensure the normal energy supply within cells.
Other potential benefits
In addition to the above-mentioned important roles, some studies have also found that glutathione may also play a certain role in improving skin health.
It can achieve the effect of whitening and fading spots by inhibiting the activity of tyrosinase and reducing the synthesis of melanin.
For some people with chronic diseases (such as diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, etc.), an increase in glutathione levels may help improve their condition and alleviate symptoms.
What are common types of glutathione nutritional supplements?
Reduced glutathione
(GSH or L-glutathione, active form)
This is the main active form in which glutathione functions in the body.
Reduced glutathione supplements can be directly absorbed and utilized by the human body, rapidly increasing the level of glutathione in the body and exerting antioxidant and detoxification effects.
Its advantage lies in its high biological utilization rate and relatively significant effect.
Oxidized glutathione
(GSSG, inactive form)
Oxidized glutathione needs to undergo a reduction reaction in the body to be converted into reduced glutathione before it can exert its function.
Compared with reduced glutathione, its bioavailability is lower and its effect may be relatively weak.
Liposomal glutathione
Liposomes are a special dosage form that encapsulates glutathione within a lipid bilayer membrane.
This wrapping method can protect glutathione from being destroyed in the gastrointestinal tract, improve its stability and absorption rate, and the absorption effect of liposomal glutathione is relatively good.
N-acetylcysteine (NAC
NAC is a precursor of glutathione. After oral administration, it can be converted into cysteine in the body and thereby participate in the synthesis of glutathione.
Although NAC does not directly supplement glutathione, it can indirectly increase the level of glutathione in the body by promoting its synthesis.
Can glutathione be obtained from food?
The answer is affirmative.

Diet is an important first step to increase and maintain glutathione levels by consuming foods rich in selenium, sulfur, zinc and precursors of alpha-lipoic acid.
Although the human body can synthesize glutathione by itself, obtaining it from food is also an important way.
Many natural foods are rich in glutathione or its precursor substances.
Animal livers are good sources of glutathione, such as pork liver, beef liver, etc. Oysters and other seafood, eggs and Brazil nuts are all rich in glutathione.
Cruciferous vegetables such as kale, arugula, broccoli, cauliflower and cabbage, as well as fruits like oranges and strawberries, all contain a certain amount of glutathione or nutrients that help synthesize glutathione. For instance, broccoli is rich in sulfur, which is one of the essential raw materials for the synthesis of glutathione.
Glutathione is also rich in yeast and wheat germ.
However, it should be noted that during the processing and cooking of food, glutathione in it may be damaged to a certain extent. For instance, high-temperature cooking can reduce the content of glutathione in food.
Therefore, in order to better retain glutathione in food, we should try to choose healthier cooking methods such as steaming and boiling.