important role of glutathione in human body
Glutathione can protect the liver because it is an antioxidant that can inhibit the generation of free radicals and reduce the damage of free radicals to liver cell membranes.
Glutathione can also promote the synthetic function of the liver, replenish the loss of glycine and taurine in liver diseases, and improve fat metabolism and the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins.

However, its significant role in the human body goes far beyond this. Today, let's take a good look at the powerful functions of glutathione.
What is glutathione?
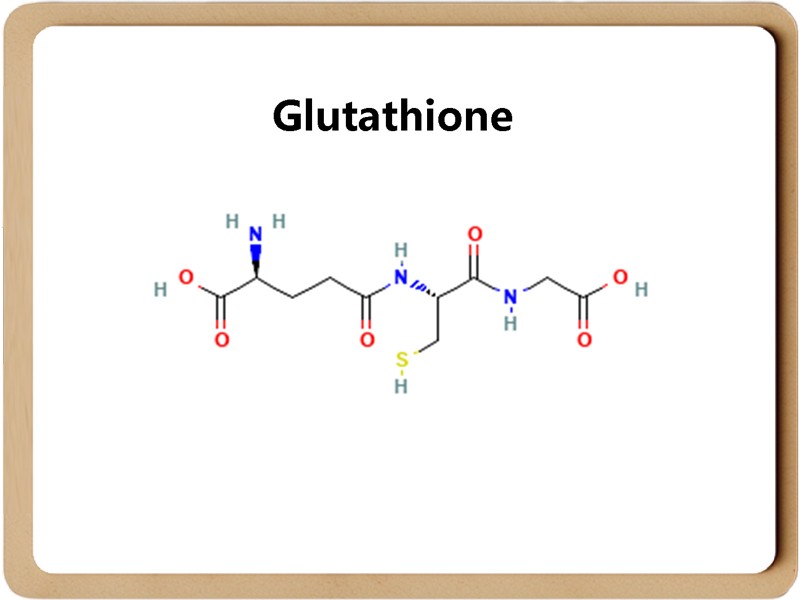
Glutathione is a tripeptide composed of glutamic acid, cysteine and glycine, containing a thiol group. It has antioxidant and integrated detoxification effects.
The thiol group on cysteine is the active group of glutathione (hence glutathione is often abbreviated as G-SH), which can easily combine with certain drugs (such as paracetamol), toxins (such as free radicals, iodoacetic acid, mustard gas, lead, mercury, arsenic and other heavy metals), etc., and thus has an integrated detoxification effect.
Therefore, glutathione (especially the glutathione within liver cells) can participate in biotransformation, thereby converting harmful toxins in the body into harmless substances and excreting them from the body.
Glutathione can also help maintain the normal function of the immune system.
Glutathione has two forms: the reduced glutathione form (G-SH) and the oxidized glutathione form (G-S-S-G). Under physiological conditions, the reduced form of glutathione accounts for the vast majority.
Glutathione reductase catalyzes the interconversion between the two types. The coenzyme of this enzyme provides NADPH for the bypass metabolism of phosphosugar.
physiological functions of glutathione
Excessive free radicals produced by the metabolism of neogenesis in the body can damage biological membranes, attack macromolecules of life, accelerate the aging of the body, and induce the occurrence of tumors or atherosclerosis.
Glutathione plays a significant role in the biochemical defense system of the human body, mainly with functions such as eliminating free radicals, enhancing the body's immunity, detoxification, and anti-aging.
1. Antioxidant and free radical scavenging
Glutathione plays a significant role in the human biochemical defense system and has multiple physiological functions. Its main physiological function is to eliminate excessive free radicals in the human body, thereby delaying skin aging.
2. Enhance body's immunity
Glutathione can not only eliminate free radicals in the human body, but also enhance the body's immunity.
Glutathione can enhance the function of T lymphocytes in the body and promote the synthesis of immunoglobulins, thereby improving the body's immunity. It can be used to treat certain allergic diseases, such as allergic rhinitis, allergic dermatitis, urticaria, etc.
3. Detoxification
Glutathione can combine with toxic compounds, heavy metal ions or carcinogens that enter the human body and promote their excretion, playing a neutralizing and detoxifying role.
4. Anti-aging and whitening
It can inactivate the activity of tyrosinase, inhibit the production of melanin, weaken the biochemical activity and formation of melanocytes, and also enhance the function of vitamin C in the body, having a whitening effect.
5. Anti-allergy
Glutathione can inhibit the allergic mediators released by histamine, thereby alleviating allergic symptoms and helping to improve skin itching, rashes and other symptoms caused by allergic diseases. It can be used for rashes caused by certain allergies.
6. Radiation protection
Glutathione has a powerful protective effect on symptoms such as leukopenia caused by radiation and radioactive drugs.
7. Protect thiol groups of proteins
Glutathione protects the -SH group in enzyme molecules, which is conducive to the exertion of enzyme activity and can restore the activity function of the -SH group in the enzyme molecule that has been damaged, enabling the enzyme to regain its activity. It can also inhibit fatty liver caused by ethanol damaging the liver.
Glutathione can also protect hemoglobin from oxidation by hydrogen peroxide, free radicals, etc., thus enabling it to continuously and normally perform its ability to transport oxygen.
The content of glutathione in human red blood cells is very high, which is of great significance for protecting the sulfhydryl groups of proteins on the red blood cell membrane from a reduced state and preventing hemolysis.